Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
If you’ve found your way here, you probably have a fruit tree. Or, you want to have one. Maybe you’ve already been growing fruit for a few years.
Related Articles
Providing frost shelter for fruit trees
Learn how to provide frost shelter for your fruit trees in spring to protect the flowers and fruit from damage.
How to buy a good fruit tree
Learn how to select a healthy fruit tree when you’re buying from a nursery, to give your trees the best possible start in life.
3 simple ways to improve your soil
Here are 3 simple ways to kickstart the health of your soil to help you grow fruit that is full of vitamins and minerals.
Whichever camp you’re in, fruit growing can feel very overwhelming. There’s so much to think about and a never-ending list of things to learn.
So, in this blog, we’re going right back to basics to help reduce the overwhelm.
Table of contents
- 1. Planning your fruit tree garden
- 2. Choosing the right types of fruit to grow
- 3. Soil and feeding your fruit trees
- 4. Weather and climate
- 5. Irrigation water and drainage for fruit trees
- 6. Thinning
- 7. Pruning fruit trees
- 8. Pests and diseases
- 9. Harvest – picking, and storage
- 10. Creating your ideal homesteading lifestyle by preserving fruit
1. Planning your fruit tree garden
Depending on your climate, it’s possible to harvest from your fruit trees for at least 6 months (or more).
But it takes good planning. Even if you already have fruit trees, planning is an activity we recommend you spend some time on each year.
You’ll get much more (both fruit and satisfaction) from your trees if you don’t just “plant and forget”. Review your fruit needs and how the trees are performing each year. Then you can adjust accordingly with more trees, fewer trees, new varieties, or solving why a tree is consistently un-fruitful, for example.
If you’re in the fortunate position of beginning your planning before you’ve planted a single tree, first you need to consider your climate. Is it temperate, arid, or subtropical, for example?
Next think about the amount of space you have, access to water, and your capacity to look after the trees.
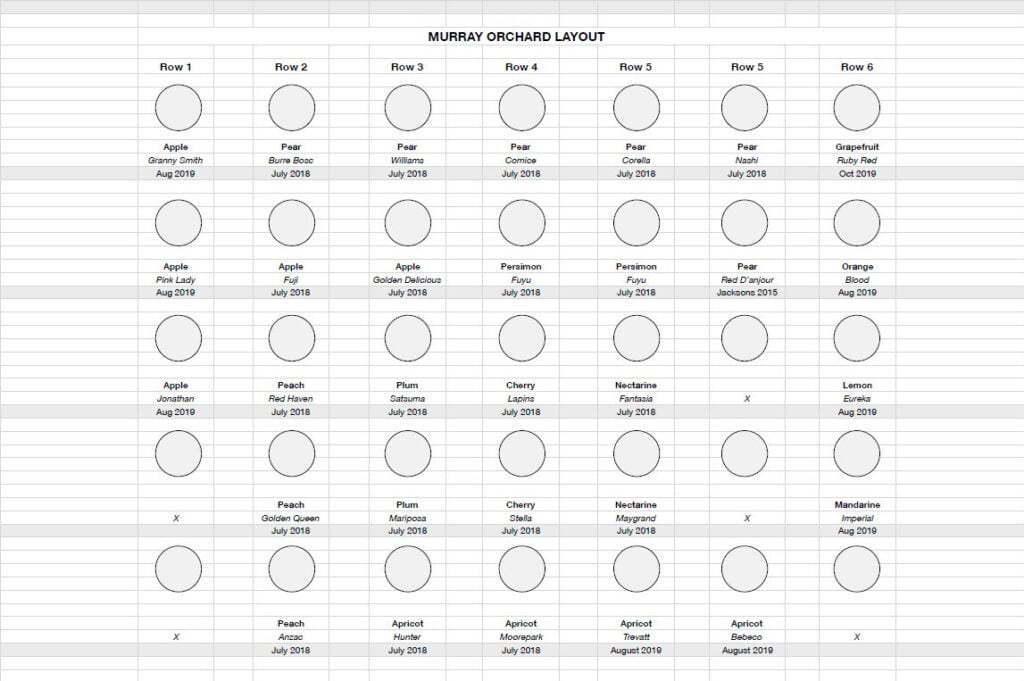
Next, ask yourself what you actually want from your fruit trees.
How much fruit do you need? What types? Do you just want fresh fruit to eat in summer, or will you be preserving it as well? Would you like to make an income from your fruit trees?
All important questions to answer before you move on to…
2. Choosing the right types of fruit to grow
There are hundreds of different types of fruit to choose from. We recommend starting with the more common fruits that are likely to grow well in your climate, and that you’re likely to eat.
Deciduous fruits are a good place to start because they thrive in a wide variety of climates. There are also many low-chill varieties available these days that suit sub-tropical regions.
Common deciduous fruits include:
- pome fruit like apples, pears, quinces, and crabapples
- stone fruit such as peaches, nectarines, plums, apricots, and cherries
- berries including raspberries, blueberries, mulberries, strawberries, blackberries, and loganberries
- other tree fruits like figs, feijoas, guava, persimmon, pomegranate, or loquat
- vine fruit like passionfruit, kiwifruit, and grapes
You may also want to expand the idea of “fruit” to include:
- nuts, including almonds, walnuts, pecans, hazelnuts, macadamia, and pistachios
- olives, and
- avocados
Citrus are evergreen (not deciduous) but will also grow in most environments, given the right conditions. Citrus trees are a practical addition to your orchard because they can extend the fresh fruit season by many months. There’s also a good selection to choose from:
- oranges
- mandarins
- cumquat
- lemons
- grapefruit
- limes
Once you have the basics covered, expand the selection to match the space you have available. If you live in a more subtropical environment, your choice expands dramatically to include fruits like:
- mango
- bananas
- custard apples
- lychees
- starfruit
- papaya
- longan
- jackfruit
- jaboticaba
- dragonfruit
However, don’t be tempted to plant more trees than you can realistically look after. Gluts of fruit and uncared-for trees can create problems and allow pests and diseases to build up.
3. Soil and feeding your fruit trees
Wherever you live, and whatever you’re planning to grow, soil is absolutely key to your success.
The principles of building healthy soil are the same whether you’re starting with sand, clay, or shale.
Soil needs organic matter, plants, microbes, moisture, and air.
It’s also possible to grow trees hydroponically, but we’re not big fans of the technique.
Why not?
For the same reasons, we don’t recommend artificial fertilisers. Fruit trees have co-evolved over millions of years with microbes that live in the soil.
The microbes get food from the fruit tree roots, and in return, they deliver nutrients to the fruit trees.
It’s called the Natural Fertility System. If the conditions are right it works perfectly and results in highly nutrient-dense food, because the tree gets exactly the nutrients it needs, at the right time.
Providing a never-ending supply of water-soluble nutrients (through artificial fertilisers or hydroponics) is like feeding your fruit trees with junk food.
The trees are much more prone to getting pests and diseases, and the fruit can be lacking in nutrition.
4. Weather and climate
Weather is one of the biggest risks when it comes to growing fruit.
Too much rain, not enough rain, hail, drought, and storms can all impact – or even destroy – your crop.
You can’t control the weather, but that doesn’t mean you can’t protect yourself against the risks.
Want to know the secret?
It’s diversity.
Building diversity into your garden at every level is your best bet at harvesting a crop from your fruit trees every single year.
Diversity means having multiple:
- types of fruit
- understorey plants including flowers, vegetables, herbs, shrubs, or even weeds
- water sources
- inputs like compost, worm castings, manures
- microbes in the soil
- animals like birds, lizards, insects
The more complex your garden is, the better protected you’ll be.
5. Irrigation water and drainage for fruit trees
Fruit trees need the right amount of water. Not too much, and not too little. Soil microbes need the same conditions.
There’s a term for it. It’s called “readily available water” or R.A.W.
Your goal is to keep the soil moist during the growing period, but also draining well enough so the trees are never sitting in pools of water for too long.
If that happens, they can drown and die in a very short time. In fact, it’s one of the most common causes of ‘unexplained’ tree death.
The techniques you use to maintain R.A.W. in your soil will be a combination of:
- natural rainfall
- water supplied through an irrigation system using either town water, dams, bores, or tanks
- landscaping features like swales
- groundcover plants to make sure the soil doesn’t dry out
- good drainage to make sure rainfall drains away from your trees
- and most important of all – great soil!
6. Thinning
We won’t go too much into thinning here, because we’ve covered it in detail in this blog.
You really just need to know that thinning is one of the most important fruit-growing techniques that you’ve probably never heard of.
Look it up in spring!

7. Pruning fruit trees
The most important pruning you’ll ever do on your fruit trees is just after you plant them. This stage is called establishment pruning, and it creates the shape your tree will have for the rest of its life.
Once established, most fruit trees need pruning once a year. This is called maintenance pruning. It keeps trees growing in the right shape, helps them to stay fruitful, and keeps the fruit growing where you can reach it.
The other main type of pruning is called renovation pruning. This may be what’s needed if the maintenance pruning has been neglected for too long and the tree has turned into a bit of a monster.
8. Pests and diseases
One of the biggest challenges you’ll have with your fruit trees is keeping them free from pests and diseases. That’s why we offer a free webinar on this topic.
But it’s not actually as hard as you might think.
As with every aspect of fruit growing, if you get the basics right a lot of potential problems just disappear.
It’s also important not to panic every time you see an insect on your trees. Just because there’s a bug there doesn’t mean it’s necessarily doing anything bad to your trees.
But how do you tell the difference?
It’s great to notice the bugs, but in a way, it’s more important to monitor your fruit, and your fruit trees, for damage.
Responding to actual damage (or even better, learning how to anticipate and prevent it in the first place) is a much better use of your energy than worrying about every insect you see.

9. Harvest – picking, and storage
Picking your fruit at the right stage of ripeness can make a huge difference to your results.
Fruit picked before it’s ripe will taste terrible – what a waste! And if it’s picked before it’s even mature, it won’t ripen off the tree.
Fruit left too long on the tree can also lose both flavour and texture, making it less pleasant to eat. And overripe fruit almost certainly won’t keep as well.
So, when it comes to picking there’s definitely a sweet spot (pun intended!).
The right time to pick each tree will depend on the variety, your climate, and the micro-climate the tree is growing in. The best way to refine this important skill is to keep a record of your picking dates each year.

10. Creating your ideal homesteading lifestyle by preserving fruit
Preserving doesn’t suit everyone. But if the idea excites you, we definitely recommend giving it a go.
There are lots of different types of preserving, including bottling (canning), drying, freezing, jams, jellies, chutneys, fruit leathers, vinegars, or fruit preserved in alcohol.
The point is to find a way to store your precious harvest to eat in the off-season. If you can preserve your fruit in a way that maintains as many nutrients as possible, all the better.
It’s also a great way to use up the second-grade fruit that you might not want to eat fresh.
Fruit preserving is incredibly satisfying – there’s nothing quite like that homesteading glow, right? And it’s genuinely rewarding to eat home-grown fruit in the depths of winter.
It’s also the last step in your fruit-growing “closed-loop” because the scraps can go into the compost or worm farm, where they’re turned back into fertiliser for your fruit trees.
And so the cycle continues…

Related Articles
Providing frost shelter for fruit trees
Learn how to provide frost shelter for your fruit trees in spring to protect the flowers and fruit from damage.
How to buy a good fruit tree
Learn how to select a healthy fruit tree when you’re buying from a nursery, to give your trees the best possible start in life.
3 simple ways to improve your soil
Here are 3 simple ways to kickstart the health of your soil to help you grow fruit that is full of vitamins and minerals.







I couldn’t find when to feed your citrus trees or fruit trees, in this blog. Do you feed your fruit trees?
Hi Caraline, yes we do recommend feeding citrus trees, in fact, they’re heavy feeders, and it’s a good idea to feed them at least a couple of times a year. You might find this blog with more info on natural fertility systems answers your question about what and when. Thanks, Meg – Grow Great Fruit team.
Really helpful tips thank you for sharing.
We have planted 10x peach 2x apricot, 1 apple, 1x medlar, 2x plums and 2x nectarines so we need all the help we can get. ;))
We retired from the UK and moved to Bulgaria so a huge change for us.
Thanks again to you both and the team.
Haven’t planted a tree, just getting the soil/planting site ready, What time of year do you plant trees?
Hi Helen, depending on where you live and on the variety of tree, the best time of year is usually winter when the trees are dormant. Cheers, Meg – GGF team.
What went wrong? Our orange tree was covered with blossoms until most (95%) fell off. Should we have fertilised the tree in spring perhaps?
Hi James, it sounds as though your tree may have suffered from some water stress, so too dry or too wet, or more likely too much variation, so wet followed by dry followed by wet again and so on.